The ecommerce space has grown substantially in recent years. In 2020, Statista recorded over two billion online purchases. More and more businesses of all sizes have migrated to digital stores and platforms to run their businesses, and many enterprises have found their inception on the ecommerce landscape. While digital developments and transactions present endless possibilities for profitability and expansion, they also come with some treacherous downsides.
Criminals, hackers, and other digital fraudsters have become increasingly common, and cybercrime has evolved into an issue that all businesses should prioritize. The first quarter of 2020 alone saw a hike in data breaches of 273%, reflecting the great upsurge in cybercrime as more businesses move to the online space. This is even more important for ecommerce business owners as the online sales journey offers numerous opportunities for cybercriminals to take advantage of.
Fortunately, there are several simple methods that you can take to protect your ecommerce store. And they don’t even need to cost you an arm and a leg. This article will explain these preventative measures to you, define ecommerce security, show you why it’s important, and discuss the common cybercrime attacks that your business should look out for.
What is ecommerce security?
Ecommerce security refers to the guidelines that guarantee safe transactions on online platforms such as ecommerce stores. These protocols safeguard both the seller and buyers’ assets from unauthorized access. Ecommerce security measures protect the safety and information of an ecommerce website’s visitors, users, and owners, and includes software solutions and tech platforms as well as practical steps and behaviors.
The importance of ecommerce security
It’s often overlooked for other features like the store design and product storefront, but security is arguably one of the more important features of your ecommerce website. Your store handles various forms of data belonging to your businesses, alongside your customer data and information.
Your customers use their credit card and banking details—among other data like their physical addresses—to complete transactions. Having a good customer engagement software and client journey map template to monitor important stops in your clients’ purchasing journeys can aid their digital security.
All of this data is placed at risk if you’re running an ecommerce store without proper and adequate security. Both your business and your customers can be under threat of identity theft, credit card theft, and fraud. This can have substantial financial repercussions for your company as you can lose large amounts of money—from the crime itself as well as the resources you will have to use dealing with the attack’s aftermath.
However, the potential damage is not just financial. Poor security and the losses experienced by your customers will negatively impact your customer relationships. This will certainly affect your customer retention and eventually, your business’ growth and bottom line. Thus, failing to invest in your ecommerce platform’s safety and security impacts your brand image and reputation. No customer wants to make purchases if they do not feel safe.
7 common ecommerce platform security attacks
When it comes to digital attacks, cybercriminals certainly know how to get creative. There are a myriad of techniques that they can use to attack your website—possibly too many for you to prevent all of them. There are, however, more common cyberattacks that businesses often experience, and here are the seven most common:
1. Malware
Malware and ransomware infections can disable you from accessing important information, data, and digital infrastructure. Hackers access your ecommerce website and its accompanying code, infecting it with malware code that targets site visitors’ personal data and your business’ data, too. Malware infections can also affect data on the devices used to visit your website.
2. Phishing
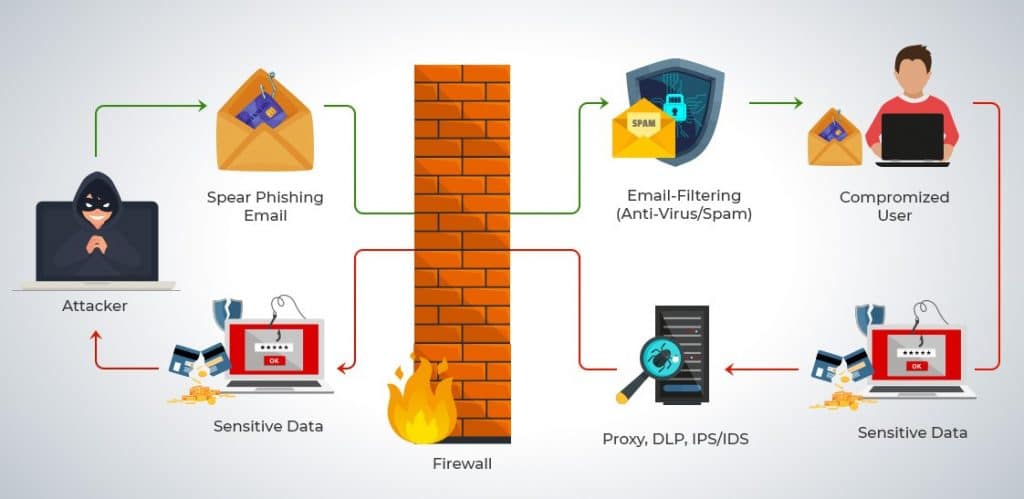
Customers sometimes receive fake messages, emails, and other communications that are supposedly coming from your company. This is known as phishing, a technique used by cybercriminals to con people out of their money by pretending that they are a trustworthy platform. Check out the latest phishing statistics to keep your customers secure in the digital world. Customers believe in the legitimacy of the communications as it uses a business phone system containing your company’s business name. Phishing attempts can include bad links to malicious URLs, where customers’ data is fraudulently extracted.
3. Cross-site scripting
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a more targeted attack that affects a web page rather than the entire website. It involves the client-side insertion of malicious code into the page.
Another distinction of this attack is that it doesn’t affect the website itself. Instead, hackers use it to target website visitors specifically. While it may change some content on your site, your website is primarily used as a vehicle to direct the malicious code to users. XSS code exposes your visitors to other kinds of attacks like phishing, malware, and others.
4. SQL injections
Some ecommerce websites record and store information in an SQL (structured query language) database. SQL is a coding language used to control databases and complete commands like data erasure. Through SQL injections, attackers can command your database to give them access to private data. Not only can they gain access to see your data, but they can also potentially alter it.
Three common SQL injections faced by websites are in-band SQL injections, inferential SQL injections, and out-of-band SQL injections.
5. DoS and DDoS
These two attacks target your website’s performance and your ability to operate online in a more direct manner.
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks shut down your website and render it unable to function. Fraudulent traffic spams your site, slowing it down and preventing actual visitors from accessing it.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks also slow down your site and clog up its traffic. DDoS attacks operate through botnets.
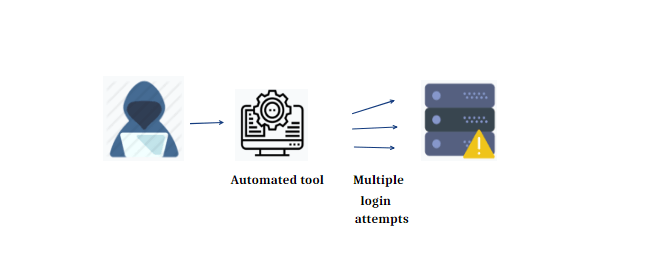
6. Brute force attacks
There are several different types of “brute force” attacks that hackers can use, including “exhaustive key search”, where the computer tries every possible combination for every character until they crack the correct password. This brute force attack relies on the speed of newly manufactured computers to decrypt a weak password.
Credential recycling is another tactic, where usernames and passwords stolen from other breaches get recycled in an attempt to break into more sites. Botnets extract the administration credentials of your website. As stated in the 2020 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, brute force tactics account for over 80% of breaches in hacking.
7. E-skimming
E-skimming is when cyber attackers steal credit card information via the payment processing page on an ecommerce site. Hackers inject a skimming code and then record the payment information of a shopper in real-time. Hackers also use phishing or a brute force attack to gain access to other sensitive information such as date of birth and location of your customers.
How to secure your ecommerce store: 7 tips
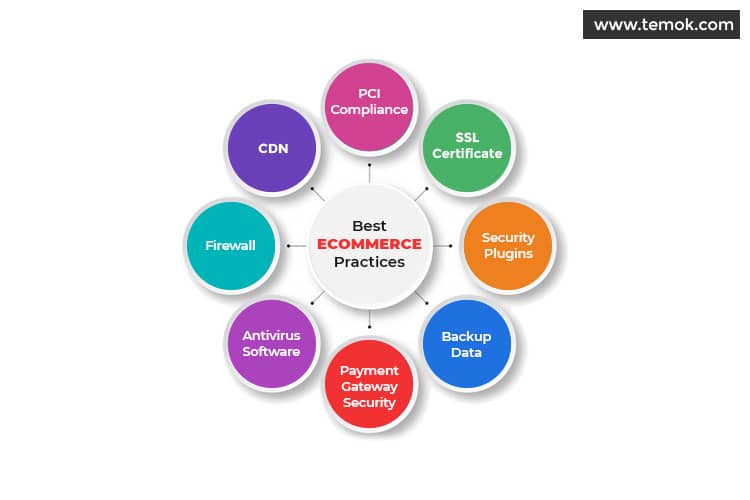
Tip #1: Find third-party payment vendors
The best way to avoid any breaches of security is to avoid storing personal customer data on your site. Use third-party payment vendors that encrypted checkout channels to process payments. Try to use a payment platform that is compatible with your ecommerce host.
This ensures your business isn’t in violation of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). PCI DSS requires customer personal data protection in the payment card industry. Having PCI DSS accreditation also establishes that your site is safe and secure for online money transfers.
Tip #2: Update your ecommerce site regularly
A common issue is that businesses do not update their sites with the latest security patches, leaving them vulnerable to security breaches. Updating your store’s software ensures its protection and minimizes the threat of attacks from malware and viruses.
Tip #3: Use a unique password for the site
Having a unique password for the site minimizes the risk of your site getting targeted through brute force attacks. Weak and compromised passwords are responsible for 81% of hacking-related data breaches, so be sure to use complex and distinct usernames and passwords.
Avoid using default passwords and previously used login credentials for your ecommerce site. Consider increasing password length and contemplate using a password manager, which saves and syncs all your private details for all the different sites and apps you use to engage customers.
You should also set up a sample communication plan to track who has access to important details and how you share passwords securely. Consider these 4 cool ways to use file-sharing in your RingCentral app.
Tip #4: Buy a secure socket layer certificate SSL
An SSL (secure socket layer) certificate certifies the identity of a website and enables an encrypted connection. It’s a security protocol that reduces the chances of data leakages as information is transferred between the customers’ devices and the webserver. Once you have an SSL certificate, you can move to a secure HTTPS hosting that protects online communications.
HTTPS is a positive communication to your customers that your site is secure, and is what it’s claiming to be. The benefits of HTTPS go beyond security and trustworthiness—it also provides a marketing boom, as secure HTTPS earns a higher search ranking by Google, leading to more traffic and potential buyers to those sites.
Tip #5: Authentication variations
Lock out users after a few failed attempts of logging in, and use a Captcha system to verify that a user is a human and not a machine. These are particularly useful at minimizing brute-force attacks.
Two-step verification requires the user to enter a one-time password delivered to your email, text, or via phone call.
Two-factor authentication asks the user to acknowledge their login attempt and authenticate this attempt through another device.
Multifactor authentication is similar to two-factor authentication, but it can require two or more steps of verification. These can range from answers to personal security questions, software tokens, and certificates, OTPs, facial recognition, and fingerprints.
These different methods offer assurances that you and approved users are the only people that can access your store site.
Tip #6: Back up your website data
Backing up your website doesn’t mean that your site is immune from breaches but it limits the damage incurred in the event of a breach. It helps protect information from being corrupted and allows you to get your site up and running as soon as possible.
Back up your ecommerce website at least once daily, and especially after an update. Another convenient method for backing up data is to use an auto-update or use a platform or web hosting site that has this as a built-in feature.
Tip #7: Website Application Firewalls (WAF)
Website application firewalls (WAFs) manage what type of traffic goes in and out of a site and intercepts any hackers or fraudulent activity. These firewalls can help take your website security to another level by protecting it from cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injections, and cross-site request forgery (CSRF/XSRF).
Website application firewalls can assist in preventing brute-force attacks, and reducing the threat of DoS and DDoS. Use WAF platforms that you’re sure of and that have verification and reviews for their capabilities, features, and the attacks these firewalls block.
A WAF is a top priority for any ecommerce business. No store owner would want to lose customers over a loss of confidential data such as financial transactions and any site data. With many WAF vendors having free trials, you can evaluate which firewall is most productive and makes the most financial sense for you.
Conclusion
All ecommerce businesses aim to offer a safe and satisfying experience for their customers. The challenge is ensuring that you implement these security measures in a way that doesn’t compromise the customer experience and that securing your site doesn’t break the bank. You can do this by using the different security practices mentioned above and keeping your site updated.
Some of these practices—and others like localization testing—can help increase consumer engagement and potentially grow your business’ revenue. Maintaining customer trust is imperative for your business’ success. Stay up to date with the latest information in the cybersecurity landscape so that you can keep your and your customers’ data safe and secure.